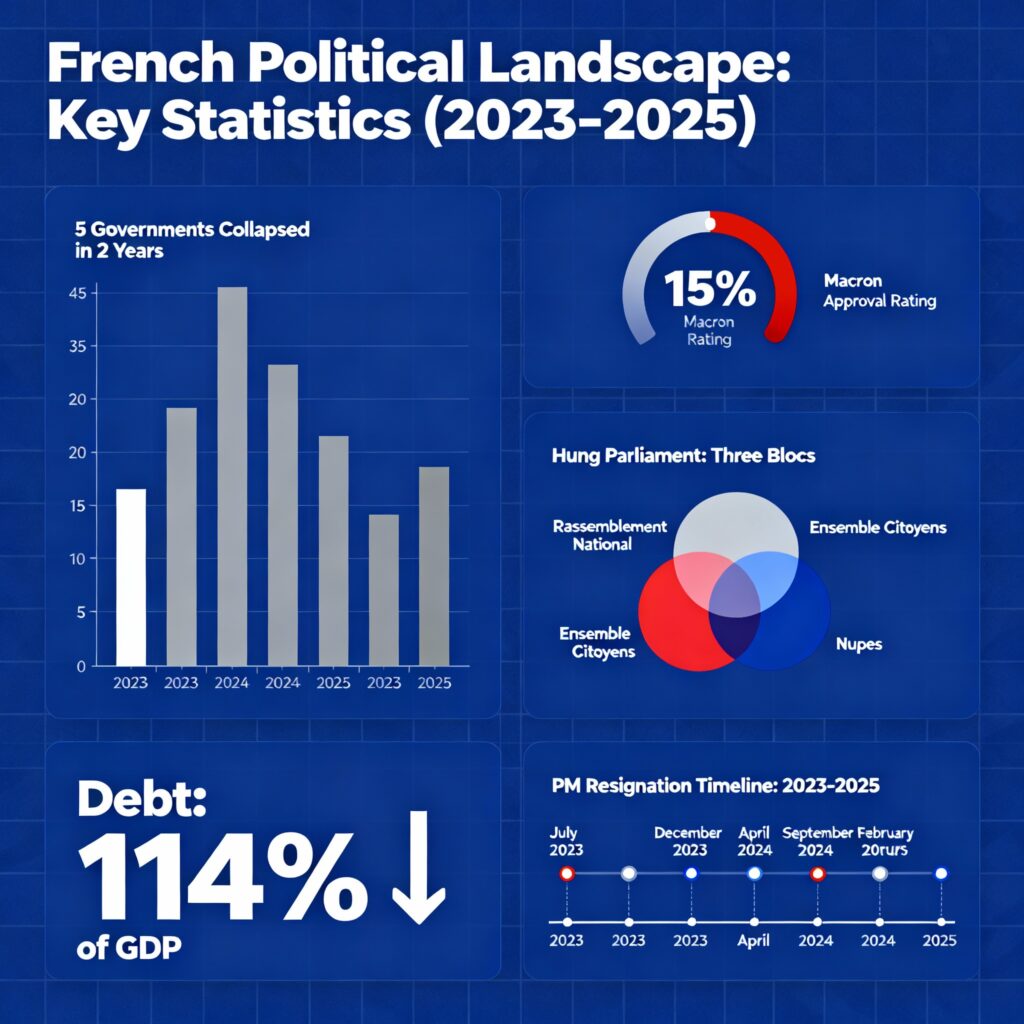
France finds itself trapped in an unprecedented political nightmare, which has transformed one of Europe’s most stable democracies into a theatre of governmental chaos. The resignation of Prime Minister Sébastien Lecornu on October 6, 2025, after serving just 26 days, making him the shortest-serving Prime Minister in modern French history, marks the France government collapse of the fifth administration in merely two years. This extraordinary political instability has sent shockwaves through European capitals and financial markets, raising fundamental questions about the sustainability of France’s Fifth Republic.

The current France political crisis represents far more than typical political turbulence; it signals a systemic breakdown of France’s governing institutions under the weight of irreconcilable political divisions, economic pressures, and President Emmanuel Macron‘s increasingly toxic brand of centrism. With France political crisis deepening by the day and no clear resolution in sight, the nation that once prided itself on institutional stability now faces the spectre of ungovernable paralysis.
The Lecornu Debacle: A Government That Lasted 14 Hours
The spectacular collapse of Sébastien Lecornu’s government represents the nadir of France political crisis, demonstrating how completely the country’s political system has broken down. Appointed on September 9, 2025, as Macron’s fifth Prime Minister in two years, the 39-year-old former Defence Minister was tasked with the seemingly impossible mission of forging consensus in a hopelessly fragmented National Assembly.
The Fatal Cabinet Announcement: Lecornu unveiled his cabinet on October 5, 2025, in what would prove to be a catastrophic miscalculation. The appointments, largely recycled from previous failed governments, immediately triggered a firestorm of criticism across the political spectrum. The decision to appoint former Finance Minister Bruno Le Maire as Defence Minister proved particularly inflammatory, given that France’s public deficit had ballooned to 5.8% of GDP during Le Maire’s tenure.
Immediate Opposition Response: Within hours of the cabinet announcement, opposition parties from both left and right declared their intention to vote down the government. Socialist leader Olivier Faure stated unequivocally that his party would vote against Lecornu “as things stand,” while Marine Le Pen’s National Rally dismissed the cabinet as “pathetic”.
The Swift Resignation: Faced with certain defeat in a confidence vote, Lecornu announced his resignation on the morning of October 6, 2025, citing “partisan appetites and failed compromises” as the reasons for his departure. His government had lasted precisely 14 hours from cabinet formation to resignation, a record that speaks volumes about the depth of France’s institutional crisis.
In his resignation statement, Lecornu blamed the political parties for acting “as though they all have an absolute majority,” highlighting the fundamental impossibility of governance in the current parliamentary configuration.
Macron’s Approval Rating Collapse: A President Without Authority
Perhaps no single factor better explains the France government collapse pattern than Emmanuel Macron’s catastrophic loss of public confidence. Once hailed as a transformative figure who would renew French democracy, Macron now governs with approval ratings that have plummeted to historic lows.
Record-Low Approval: Multiple polling organisations now show Macron’s approval rating hovering between 15-22%, representing a new low for any sitting French President under the Fifth Republic. The Odoxa polling institute’s recent survey found that only 22% of French citizens approve of Macron’s performance, while other polls suggest the figure may be even lower at 15-17%.
Loss of Legitimacy: This collapse in public support has created a fundamental legitimacy crisis for the French presidency. Opposition leaders across the political spectrum now openly question Macron’s right to govern, with far-left leader Jean-Luc Mélenchon calling for the President’s impeachment and Marine Le Pen demanding his immediate resignation.
The Toxicity Factor: Macron’s unpopularity has become so severe that association with him has become politically toxic. As BBC correspondent Hugh Schofield observes, “The president’s unpopularity means those who associate themselves with him risk a beating at France’s 2027 election”. This dynamic makes it nearly impossible for any Prime Minister to succeed.
The approval rating collapse reflects deeper issues with Macron’s governing style, which critics describe as authoritarian and dismissive of democratic consultation. His preference for “control over conversation” has alienated not just opposition parties but also potential allies.
The Hung Parliament Trap: Three Blocs, Zero Solutions
The root cause of France’s ongoing France political crisis lies in the mathematical impossibility of forming a stable government with the current parliamentary composition. The hung parliament that emerged from the June-July 2024 snap elections has created a three-way deadlock that makes effective governance virtually impossible.
The Three-Bloc Configuration: The National Assembly is now divided into three roughly equal and mutually antagonistic blocs: the New Popular Front (NFP), a left-wing coalition holding approximately 193 seats; Macron’s centrist Ensemble coalition with 166 seats; and Marine Le Pen’s far-right National Rally with 142 seats. With no bloc reaching the 289-seat majority threshold, any government requires cross-party cooperation that has proven impossible to achieve.
Ideological Incompatibility: The three blocs represent fundamentally incompatible visions for France’s future. The NFP advocates for massive public spending increases and wealth redistribution. The National Rally promotes nationalist economics and immigration restrictions. Macron’s centrists pursue austerity measures and European integration. These ideological differences make meaningful compromise virtually impossible.
Budget Paralysis: The parliamentary deadlock has created a particularly acute crisis around budget approval. France desperately needs to pass spending cuts and tax increases to comply with EU fiscal rules, but each bloc has different ideas about how to achieve fiscal consolidation.
Electoral Calculations: Each bloc is positioning itself for the 2027 presidential election rather than focusing on immediate governance needs. This electoral calculus makes compromise even more difficult as party leaders fear that cooperation might damage their long-term political prospects.
Economic Crisis Fueling Political Instability
France’s government collapse pattern is inextricably linked to the country’s deteriorating fiscal position, which has created an urgent need for unpopular reforms that no government can successfully implement.
Debt Crisis Dimensions: France’s public debt has reached alarming proportions, standing at 114% of GDP, the third-highest in the eurozone after Greece and Italy. The country’s deficit reached 5.8% of GDP in 2024, nearly double the EU’s 3% limit. These figures significantly exceed European Union regulations and have triggered warnings from rating agencies.
Rating Agency Pressure: The fiscal deterioration has prompted rating agencies to reassess France’s creditworthiness. Fitch has already downgraded France’s rating, and Moody’s is expected to follow suit by the end of October 2025. These downgrades increase borrowing costs and further constrain the government’s fiscal options.
Market Volatility: Financial markets have responded nervously to France’s political instability. Following Lecornu’s resignation, the CAC 40 index fell by more than 2%, the euro slipped to $1.1667, and the 10-year French bond yield reached 3.57%. The spread between French and German government bonds has widened to 87 basis points, reflecting growing concerns about France’s fiscal sustainability.
Austerity Resistance: The economic crisis requires significant spending cuts and tax increases, but these measures are politically toxic. Previous attempts to implement austerity measures have triggered massive protests, including the ongoing “Bloquons Tout” (Let’s Block Everything) movement focusing on economic inequality and rising living costs.
The Macron Gamble: How Snap Elections Backfired Catastrophically
The origins of France’s current France political crisis can be traced directly to President Emmanuel Macron’s catastrophic decision to call snap parliamentary elections in June 2024, a political gamble that spectacularly backfired.
The European Election Trigger: Following his party’s poor showing in the June 2024 European Parliament elections, where Marine Le Pen’s National Rally secured 30 seats out of 80 French seats, Macron made the fateful decision to dissolve the National Assembly. His stated goal was to “clarify” the political situation and potentially secure a working majority.
Strategic Miscalculation: The snap election strategy was based on the assumption that, faced with the prospect of a far-right government, French voters would rally behind Macron’s centrist coalition. Instead, the elections produced the exact opposite result: a more fragmented parliament that made governance virtually impossible.
Electoral Outcome Disaster: Rather than clarifying France’s political direction, the June-July 2024 elections created unprecedented fragmentation. The left-wing New Popular Front emerged as the largest bloc with 193 seats, but without an overall majority. Macron’s Ensemble coalition was reduced to just 166 seats, while Le Pen’s National Rally significantly increased its parliamentary presence.
Public Perception of Recklessness: French voters have largely perceived Macron’s decision to call snap elections as a reckless move that exacerbated the country’s divisions. Opinion polls consistently show that majorities blame Macron for the current instability.
Coalition Building Impossibility: The electoral outcome left Macron leading the second-largest bloc in parliament but unable to form coalitions with either the far-left NFP or the far-right National Rally.
International Implications and Future Scenarios
The ongoing France government collapse pattern has significant implications beyond French borders, affecting European Union decision-making and global financial markets.
EU Leadership Vacuum: France’s political instability has created a leadership vacuum within the European Union. With Germany facing its own challenges and France unable to provide consistent leadership, the EU struggles to maintain strategic direction.
Economic Contagion Risk: France’s fiscal crisis poses risks of economic contagion within the eurozone. As the bloc’s second-largest economy, France’s financial difficulties could trigger broader European economic problems.
Future Scenarios: Several potential outcomes could unfold: Macron could attempt to appoint another Prime Minister, though previous failures suggest difficulty; new parliamentary elections might occur after June 2025, but could strengthen extremist parties; Macron’s resignation remains possible, though unlikely; or France could face prolonged paralysis with continued governmental instability.
Conclusion: The Unravelling of the French Republic
The France government collapse crisis of 2025 represents more than a temporary political difficulty; it signals the potential unravelling of the Fifth Republic’s governing model. Sébastien Lecornu’s record-breaking 26-day tenure serves as a stark symbol of a political system that has lost the ability to govern effectively.
The convergence of Macron’s historic unpopularity, an ungovernable hung parliament, severe economic pressures, and opposition obstruction has created a perfect storm of political dysfunction. What began as Macron’s promise of a “democratic revolution” in 2017 has devolved into institutional breakdown threatening both French democracy and European stability.
The France political crisis exposes fundamental flaws in the Fifth Republic’s constitutional framework, designed for bipolar politics but unable to cope with fragmented contemporary reality. The traditional “republican barrier” against extremism has collapsed, replaced by a three-way deadlock where no group can govern but each can prevent others from doing so.
With France’s debt at 114% of GDP and deficit at 5.8%, the country cannot afford prolonged political paralysis. Yet the reforms needed to address these problems are precisely what the current configuration makes impossible to implement. This represents a crisis of democratic governance at precisely the moment when strong leadership is most needed.
As Macron approaches his mandate’s final two years, the question is no longer whether he can recover political authority, which appears impossible, but whether French democracy can survive the chaos he has unleashed. The path forward requires opposition leaders willing to put national interest above electoral calculation, a President humble enough to acknowledge failures, and French people patient enough to support difficult compromises.
Without such transformation, France risks becoming Europe’s first established democracy to succumb to the populist wave sweeping the Western world. The stakes could not be higher; France’s crisis is about whether democratic institutions can adapt to 21st-century challenges or crumble under polarisation and institutional rigidity.
